Traps are not passing through to IPHost installation, when it’s behind NAT. How to make it work?
Q: I want to set up SNMP Traps from devices behind our NAT local network. Is it possible?
A: Yes, it is possible. Depending on how IPHost interconnects to the network device in question, certain adjustments can be done.
For the sake of example, below is displayed how SNMP Trap should pass to primary installation.
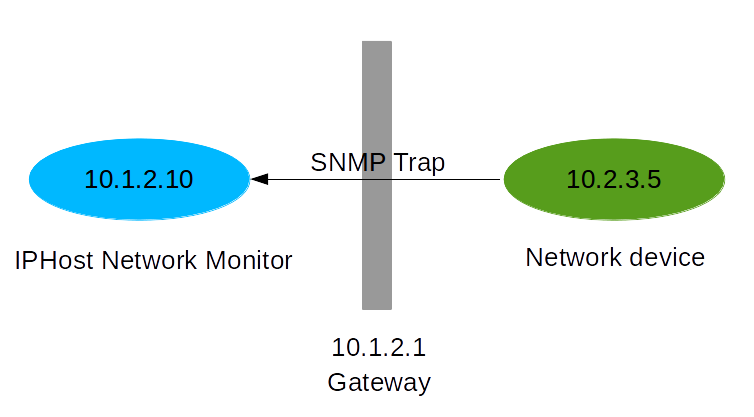
Note: when repeating the setup, please use actual IP addresses of every entity mentioned above.
Setup instructions
Case 1: IPHost network Monitor installation (10.1.2.10) can be contacted directly from network device that should send SNMP traps (10.2.3.5). If all the traffic from IPHost’s side is passing through gateway (10.1.2.1), applying NAT, you should set up trap as stated below:
1. Create host for gateway (10.1.2.1) on IPHost installation. When SNMP Trap is sent, it will look as if it comes from gateway, regardless of its actual origin.
2. Create SNMP Generic Trap monitor for the host above. Since traps will look as coming from gateway, you should use filtering SNMP Trap by payload to tell, where it actually comes from, and perform proper actions.
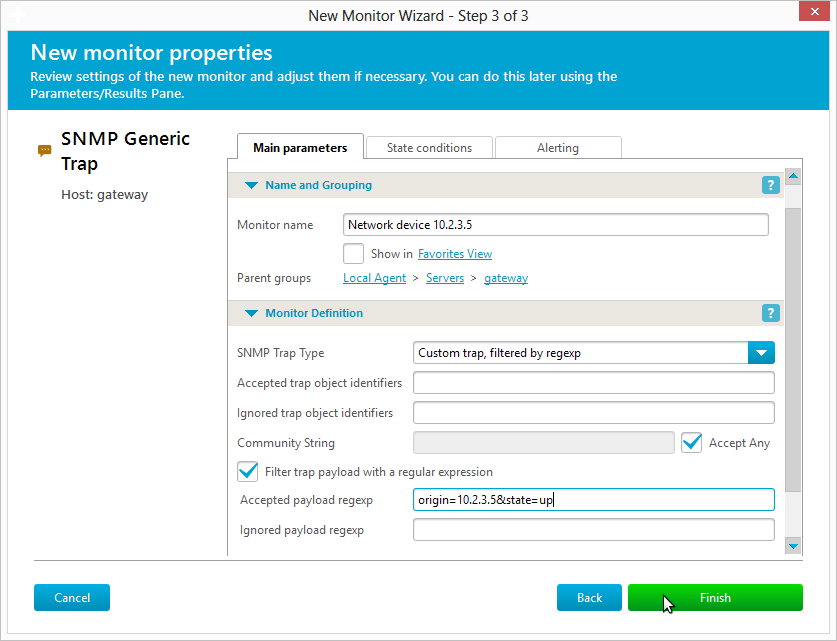
Note: in the sample setup above, trap is identified by sent variable named “origin”, containing value (payload) 10.2.3.5 – use similar approach to identify trap origin, wherever possible.
3. On network device (10.2.3.5) side: set up SNMP trap receiver as IPHost installation (10.1.2.10). Use appropriate port number (UDP 162 by default) and other SNMP parameters, as expected on IPHost installation. Important: add variable(s) to pass with trap and assign value that can be used to identify trap origin.
Case 2: IPHost network Monitor installation (10.1.2.10) cannot be contacted directly from network device that should send SNMP traps (10.2.3.5). The setup in such a situation looks like this:
1. On NAT gateway (10.1.2.1) set up port forwarding. Specify incoming port SNMP Traps should use (say, 8162) and forward it to IPHost installation and SNMP Trap port it uses (say, 162).
2. Create host for gateway (10.1.2.1) on IPHost installation. When SNMP Trap is sent, it will look as if it comes from gateway, regardless of its actual origin.
3. Create SNMP Generic Trap monitor for the host above. Since traps will look as coming from gateway, you should use filtering SNMP Trap by payload to tell, where it actually comes from, and perform proper actions.
4. On network device (10.2.3.5) side: set up SNMP trap receiver as gateway (10.1.2.1). Use appropriate port number (UDP 8162 in this example, see 1. above) and other SNMP parameters, as expected on IPHost installation. Important: add variable(s) to pass with trap and assign value that can be used to identify trap origin.
Multiple SNMP traps
When you need to use more than one SNMP Generic Trap monitor in the above situation, just add more SNMP Generic Traps using the same parameters. They should use “Filter trap payload” to look for identifying text sent along with traps, to catch trap from proper network device.

